What is ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and how does it work?
Share
More and more we're finding Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production to be a key point of discussion for both the fitness and biohacking crowds.
It's always a welcome topic of question for us in store, and for good reason given ATP's importance to all aspects of human performance and even just being alive, affecting everyone in everyone waking or sleeping second.
So with this in mind, we've prepared the following article to help establish the basics of:
- what ATP is;
- the function of ATP in all living beings;
- how ATP production is regulated;
- and what you can do to increase your own ATP production.
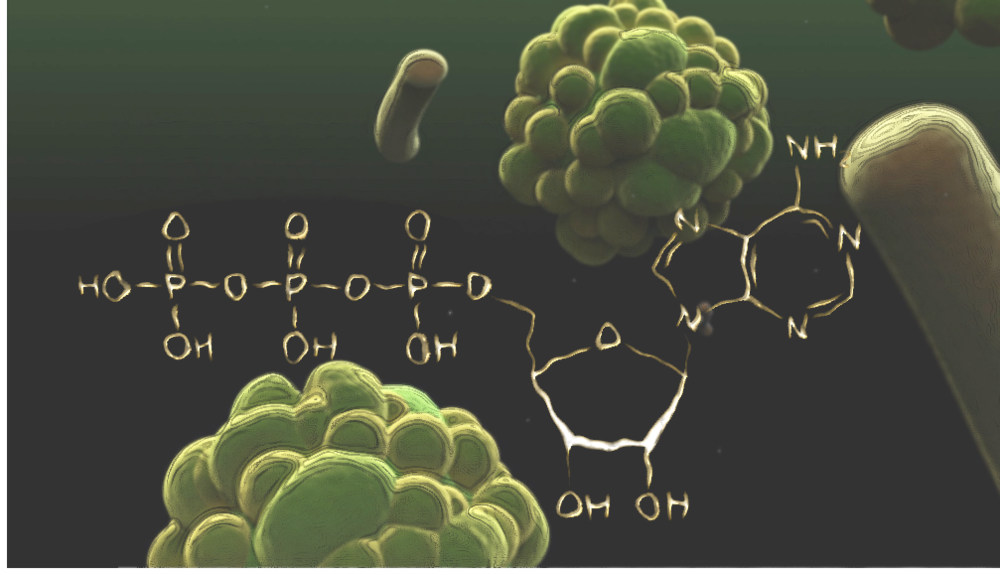
What is ATP?
ATP, adenosine triphosphate, is a naturally occurring molecule in the cells of all living organisms.
As the name reads, it is made up of one adenosine molecule and a chain of three phosphoryl groups. ATP is created by chemical processes that break down large molecules to smaller, these are known as catabolic pathways (or catabolism). This occurs at “the powerhouse of the cell” - the mitochondria!
It should be noted that ATP does not store very well, that’s why we store our energy more long term with sugars and fats.
What is ATP’s function?
One common phrase is that “ATP is the energy currency of the cell.”
But what exactly does that mean?
Essentially, ATP is used to deliver energy from energy storing processes in cells (catabolism) to energy demanding processes (anabolism).
The conversion of ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is what releases the energy. In your body, this energy can be used for everything from keeping you warm, generating forces for movement, supplying reactions to synthesise valuable chemicals, or build new cells. So if you want to do anything with your life other than degrade into a sludge...you’re gonna be depending on that sweet sweet ATP.

How is ATP regulated?
The ATP process is largely dictated by how the vital enzyme AMPK interacts with its environment. This is the tool for ATP manufacture (located within the mitochondria).
AMPK is known to be closely regulated activated by two key conditions. That being the ratio of AMP (adenosine monophosphate) to ATP molecules present, and the amount of calcium present. Other significant environmental influences are the amount of oxygen available, and the temperature. But of course, being a biological process there are a bunch of other factors that can contribute. One mechanism of popular interest is how phosphorylcreatine and creatine in the regulate ATP synthesis. [3]
Also important to note, maintaining suitable mitochondrial health is vital for manufacture as this is the host site for ATP synthesis.
What can I do to increase my ATP output?
There are a three main mitochondrial mechanisms to consider to increase ATP output.
-
Increase the ATP output of individual mitochondria though stimulation and material availability.
-
Stimulate new mitochondria growth (biogenisis) to provide more ATP processing sites.
-
Restoration and protection of mitochondria from sources of damage, ensuring proper function.
Some inputs worth looking into include:
-
Exercise - Triggers increased mitochondrial biogenisis via increased cellular energy demand. [6]
-
Near Infrared Light - Increased ATP production via mitochondrial photo-stimulation. [4, 5]
-
Heat - Improving mitochondrial health with heat shock proteins and increasing mitochondrial growth. [6, 7]
-
Cold - Trigger for increased mitochondrial growth within fat tissue via “fight or flight” response systems. [8]
-
Supplementation - Creatine, L-Carnitine, ALCAR, Cordyceps, CoQ10, Resveratrol, NAD+ pecursors NMN and NR, NAC, Riboflavin, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Alpha-Lipoic Acid, and many others have been shown to benefit ATP production through various mechanisms.
In the future we'll cover these supplements in depth, however if you want to get started on research of your own, some good starting points could be the articles referenced at the bottom of this article.
Take home message
ATP is what delivers the energy input to any energy demanding processes that your body, or any living thing uses.
Really, ATP is the input to life.
There are a number of environmental influences that regulate ATP production. Primarily having the right balance of building blocks in the local area, as well as environmental temperature. As the process takes place in the mitochondria, the health of that area is key to efficient manufacture.
There are also many ways you can increase your ATP production, including supplementation, exercise and changes to your surroundings.
What now? Do some of your own research and get the best value for your energy!
Other valuable Learning
If you’re keen to learn more in depth about what ATP is and how it operates, Khan Academy does some great videos that are friendly to any entry level audience. Check out their intro to the right.
(FYI: Nice Supplement Co. is not affiliated with Khan, we just appreciate free high, quality education!)
Or check out the articles linked below!
REFERENCES
[1] ATP synthesis and storage. (April 2012), Purinergic Signalling
[5] Biological Effects of Low Level Laser Therapy. (2014), Journal of Lasers in Medicine Sciences.
[10] Dietary Supplements for Primary Mitochondrial Disorders, National Institutes of Health.
